By recapitulating the disease features in a test platform, it is possible to effectively achieve groundbreaking patient-in-a-dish functionality. These platforms enable personalized models of the disease that can lead to life-saving and revolutionary testing of Direct Drug Response (DDR) on patient-in-a-dish, rather than the individual. Response measured from the diseased tissue is by definition more comprehensive and predictive than digital twin of a patient that is computer analysis based on a limited number of biomarkers.
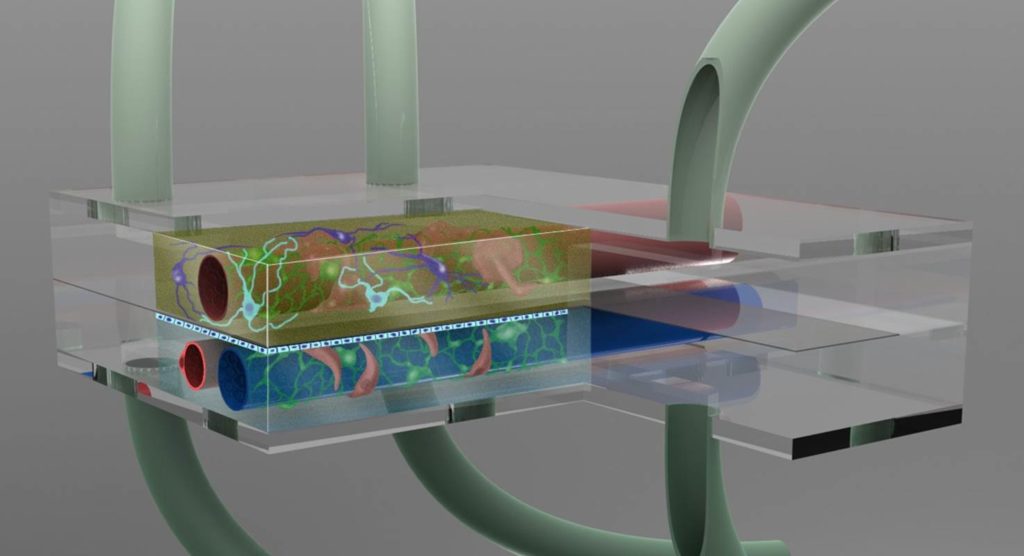
This illustration shows multiple cell types including neurons with long axons embedded in a porous gel-like matrix. Green tubes are microfluidic connections for the circulating fluid. This model allows complex interactions that represent physiology better than traditional “flat” models.
The microenvironment can be controlled in multiple ways in micro-physiological systems (MPS) that are based on microfluidics to support complex tissue in realistic conditions. First and foremost solid tissue requires constant supply of oxygen, which is as essential as nutrients supplied through an artificial circulation using microfluidics, as illustrated on the left. The extent of shear force is very important for growth of certain endothelial cells and have an impact on stem cell differentiation. Additional factors of the environment include with surface coatings and the nature of the matrix in which cells can organize themselves in 3-dimensional environments.
Finally, the source of biological material is very important. There are several constructs based primarily on the following biological entities call: spheroids, organoids, micro-slices and stem cells. Spheroids are the simplest, they are 3-dimensional constructs often with multiple types of cells, but no stem cells. Organoids are derived from patient tissue, such as biopsy, they are cultured under conditions that enhance stem cells naturally present in the tissue. This results in more self-regeneration capabilities, however, the cells may gradually drift from phenotype observed in vivo that is they drift genomically and functionally from what was originally biopsied. Micro-tissue slices overcome the challenge of stem cells drifting organoid behavior from that of the original tissue, and them also bring more of the solid tissue microenvironment (stroma) that has significant impact on behavior of cancer cells, for example. The final option of using stem cells is in principle the most general. Differentiation of stem cells is particularly favored for work with brain tissue where it is possible to grow organoid “mini-brains” for months, achieving impressive imitation of cortical growth.
Effective disease models take into account requirements of biology to simulate physiological conditions and selection of the proper hardware which is largely unknown to the broader community of life scientists. In the US organizations like the 3Rs Collaborative are promoting MPS technologies and liaising with similar initiatives in the EU among others.

